Fasiglifam
Names and Identifiers of Fasiglifam
CAS Number |
1000413-72-8 |
|---|---|
EC Number |
805-621-8 |
MDL Number |
MFCD18251445 |
IUPAC Name |
2-[(3S)-6-[[3-[2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-methylsulfonylpropoxy)phenyl]phenyl]methoxy]-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-3-yl]acetic acid |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C29H32O7S/c1-19-12-25(34-10-5-11-37(3,32)33)13-20(2)29(19)22-7-4-6-21(14-22)17-35-24-8-9-26-23(15-28(30)31)18-36-27(26)16-24/h4,6-9,12-14,16,23H,5,10-11,15,17-18H2,1-3H3,(H,30,31)/t23-/m1/s1 |
InChIKey |
BZCALJIHZVNMGJ-HSZRJFAPSA-N |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=CC(=CC(=C1C2=CC=CC(=C2)COC3=CC4=C(C=C3)C(CO4)CC(=O)O)C)OCCCS(=O)(=O)C |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC1=CC(=CC(=C1C2=CC=CC(=C2)COC3=CC4=C(C=C3)[C@@H](CO4)CC(=O)O)C)OCCCS(=O)(=O)C |
UNII |
GLP1W4JXAH |
UNSPSC Code |
12352100 |
Physical and chemical properties of Fasiglifam
Acidity coefficient |
4.36±0.10(Predicted) |
|---|---|
Boiling Point |
739.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
Density |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
Exact Mass |
524.186890 |
Flash Point |
400.8±32.9 °C |
H Bond Acceptors |
7 |
H Bond Donors |
1 |
Index of Refraction |
1.587 |
LogP |
4.36 |
Melting Point |
123-127°C |
Molecular Formula |
C29H32O7S |
Molecular Weight |
524.625 |
PSA |
107.51000 |
Solubility |
Acetonitrile (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
Storage condition |
2-8℃ |
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
Solubility of Fasiglifam
| Solvent | Dissolution Phenomenon | Temperature Effect | pH Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Insoluble or very slightly soluble | Increasing temperature slightly enhances solubility, but overall solubility remains low | Solubility slightly increases under acidic conditions (pH 1–3); solubility is lower under neutral and alkaline conditions |
| Ethanol | Soluble | Solubility increases with rising temperature | pH has little effect, as it's a non-aqueous system |
| Methanol | Freely soluble | Rising temperature significantly improves solubility | pH not applicable (non-aqueous solvent) |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) | Highly soluble (commonly used in vitro experiments) | Completely miscible at high temperatures | Hardly affected by pH |
| Acetone | Soluble | Solubility increases with rising temperature | pH effect is negligible |
| Chloroform | Soluble | Increased temperature promotes dissolution | Not affected by pH |
| Ethyl Acetate | Slightly soluble to soluble | Higher temperature aids dissolution | pH has no direct effect |
Safety Information of Fasiglifam
Key Milestone of Fasiglifam
| Time | Milestone Event | Detailed Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2004 | Compound Discovery and Initial Screening | Takeda Pharmaceutical (Japan) discovered TAK-875, a novel G protein-coupled receptor GPR40 (also known as FFAR1) agonist with potential for promoting glucose-dependent insulin secretion, through high-throughput screening. |
| 2008 | First Human Clinical Trial (Phase I) | Initiated Phase I clinical trials in healthy volunteers to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy of TAK-875. Results showed significant blood glucose-lowering effects with a low risk of hypoglycemia. |
| 2010 | Phase II Clinical Trials Launched | Conducted multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase II clinical studies in patients with type 2 diabetes. Results demonstrated that TAK-875 significantly improved HbA1c levels, outperforming placebo and some existing oral hypoglycemic drugs. |
| 2011–2013 | Ongoing Phase III Clinical Trials | Launched multiple Phase III clinical trials globally (e.g., ZEAL, SAKE series) to evaluate long-term efficacy and safety, aiming to support a New Drug Application (NDA). Data indicated good glucose-lowering effects and cardiovascular safety. |
| 2013 | Emergence of Hepatotoxicity Signals | Multiple subjects exhibited elevated liver enzymes (ALT/AST > 3×ULN) after long-term use, with some cases progressing to severe drug-induced liver injury, raising concerns about liver safety. |
| End of 2013 | Takeda Announces Termination of Development | Due to potential uncontrollable hepatotoxicity risks, Takeda Pharmaceutical announced the global discontinuation of all clinical development of TAK-875 and abandoned the New Drug Application. |
| 2014 onwards | Retained Scientific Value | Although development was terminated, TAK-875, as the first GPR40 agonist to reach advanced clinical stages, remains an important reference and structural template for subsequent GPR40-targeted diabetes drug development. |
Applications of Fasiglifam
Fasiglifam was primarily developed for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus but was also explored for potential applications in chronic kidney disease due to its effects on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Despite its promising profile, its clinical development was terminated following reports of liver toxicity during Phase III trials.
Interaction Studies of Fasiglifam
Interaction studies have revealed that fasiglifam may influence various hepatic transporters and metabolic pathways. It has shown inhibitory effects on multidrug resistance-associated proteins (MRPs), particularly MRP3, which could lead to altered bile acid transport and accumulation of toxic metabolites in liver cells. Additionally, the compound's interaction with mitochondrial respiration pathways has been studied, indicating potential mitochondrial toxicity at high concentrations.
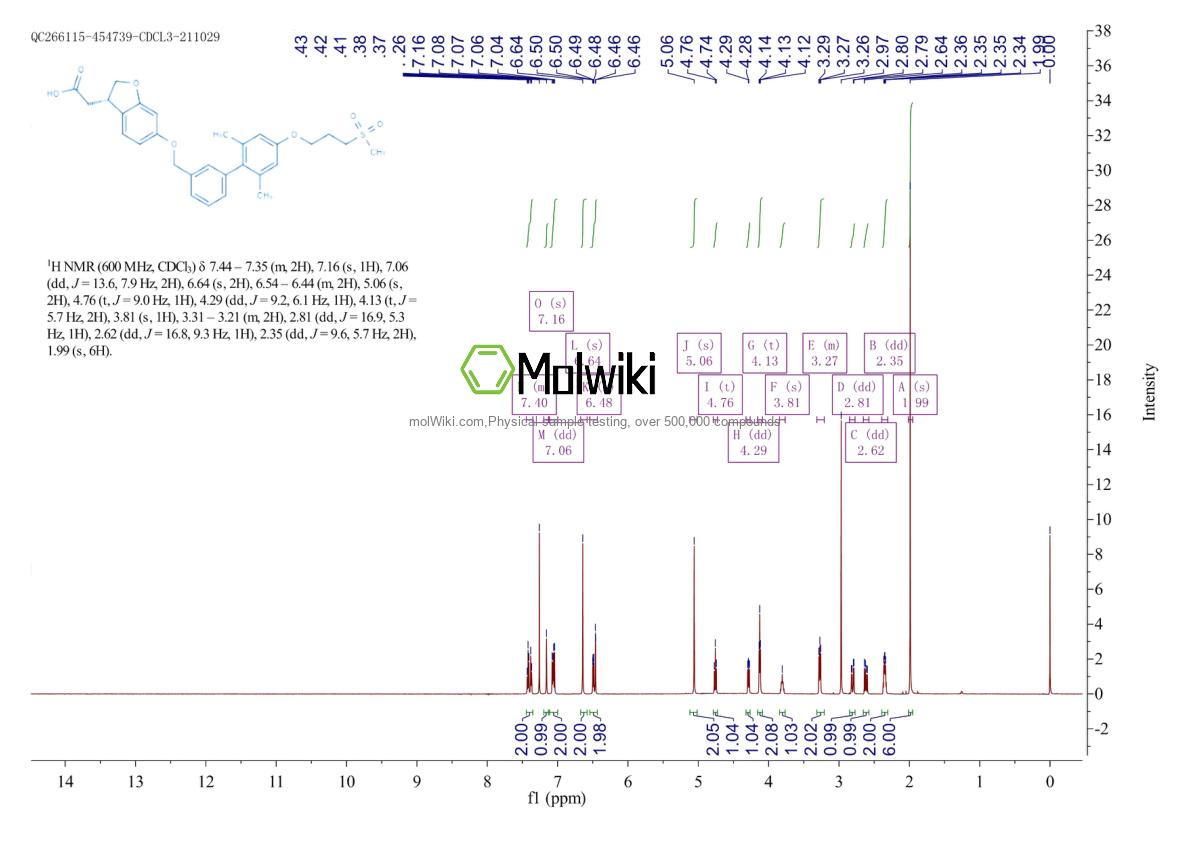
Physical sample testing spectrum (NMR) of Fasiglifam